This content is also available in: German
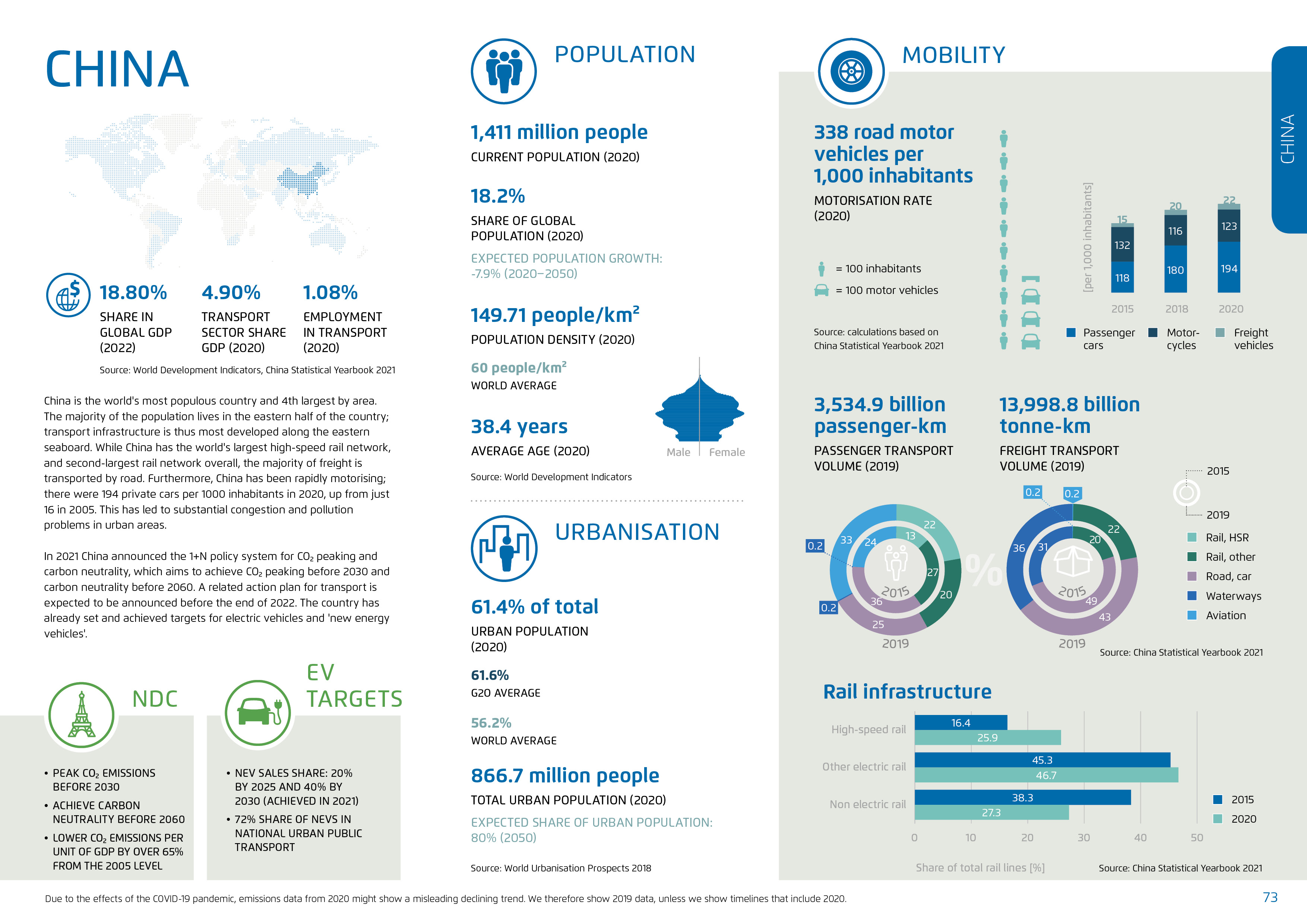
China
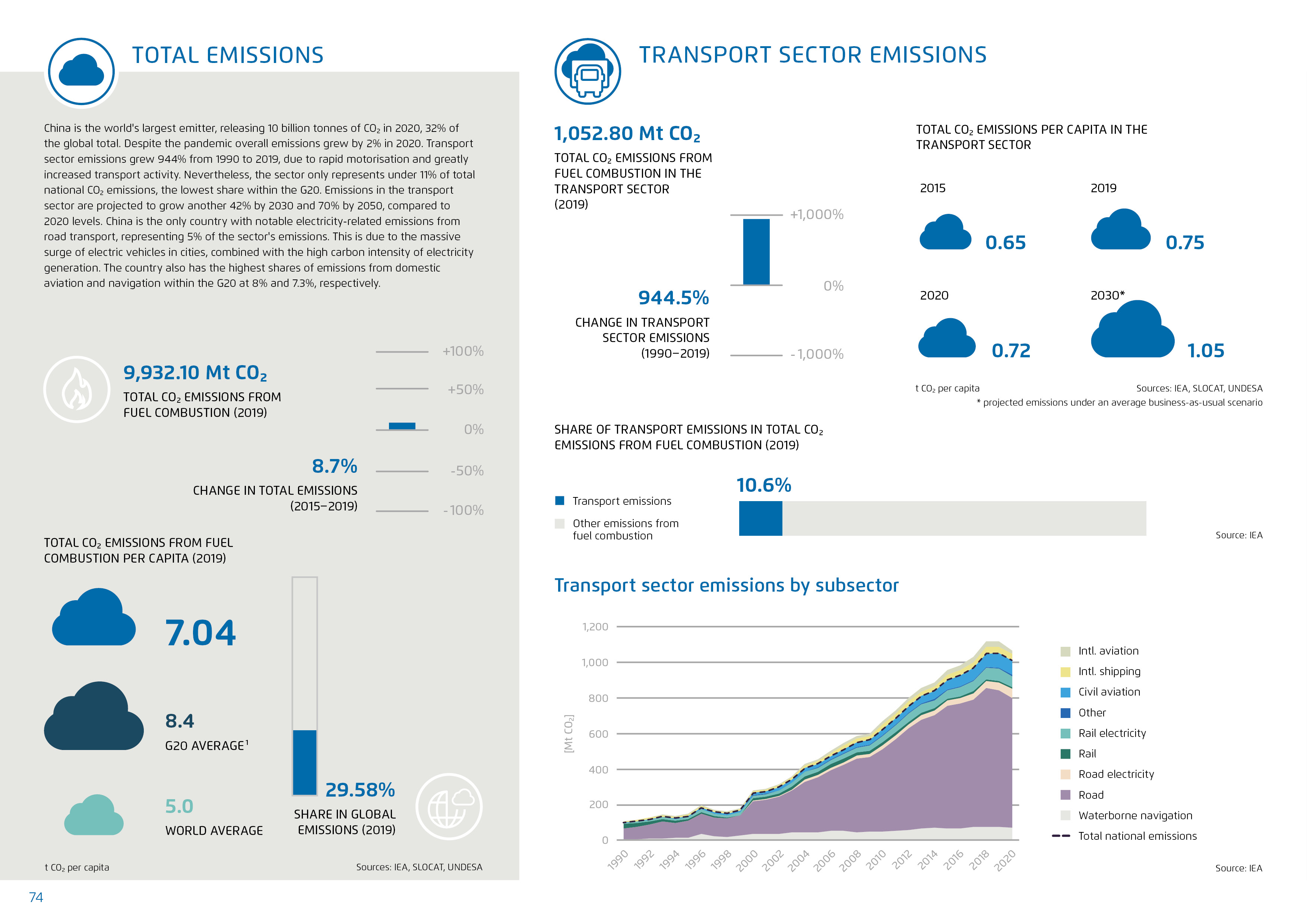
Carbon neutrality before: 2060 / Motorisation rate (2020): 338 vehicles per 1,000 inhabitants / Change in transport sector emissions (1990-2019): 944,5 % / Projected total CO2 emissions per capita in the transport sector in 2030: 1,05 t
China is the world's most populous country and 4th largest by area. The majority of the population lives in the eastern half of the country; transport infrastructure is thus most developed along the eastern seaboard. While China has the world's largest high-speed rail network, and second-largest rail network overall, the majority of freight is transported by road. Furthermore, China has been rapidly motorising; there were 194 private cars per 1000 inhabitants in 2020, up from just 16 in 2005. This has led to substantial congestion and pollution problems in urban areas.
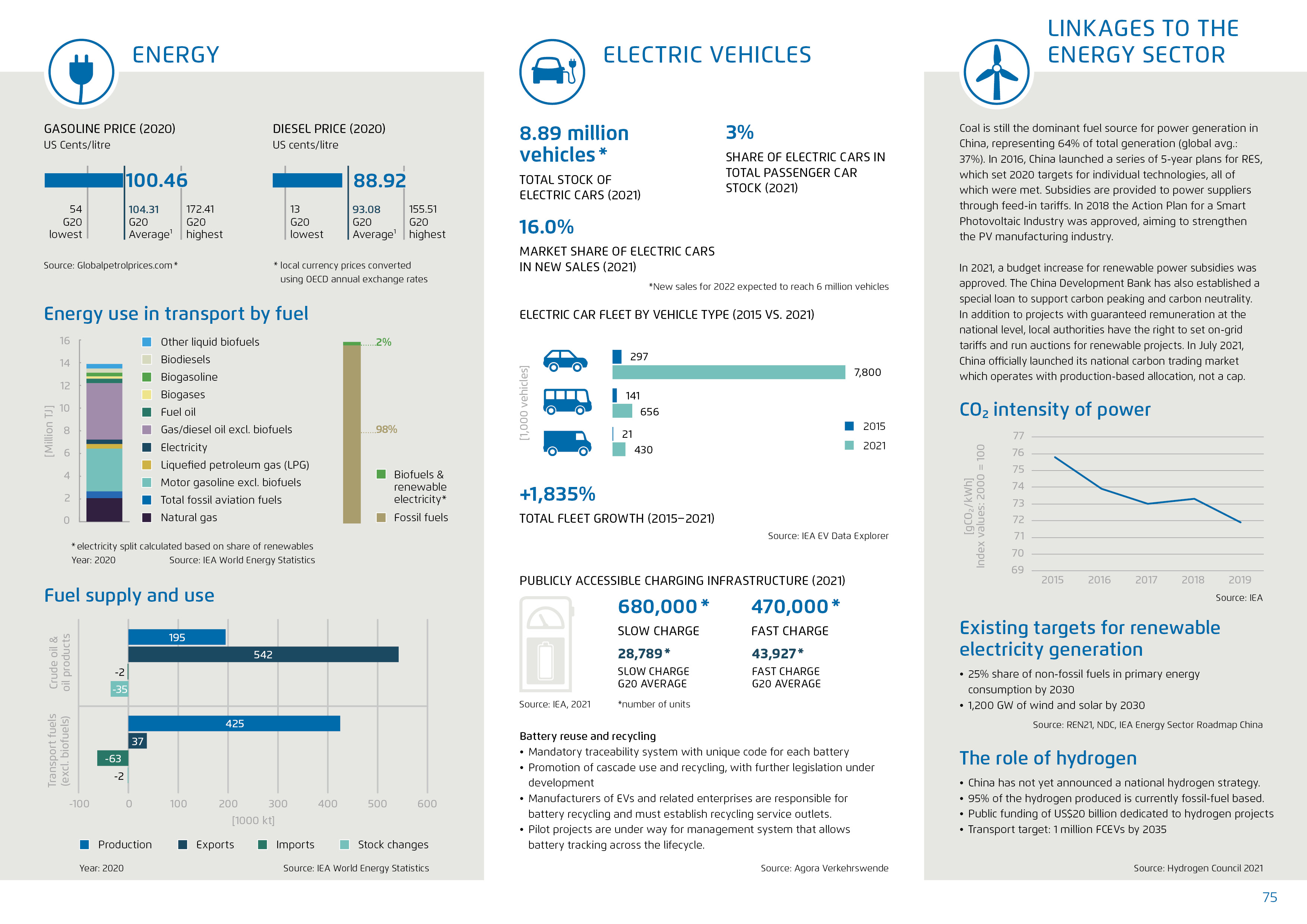
In 2021 China announced the 1+N policy system for CO₂ peaking and carbon neutrality, which aims to achieve CO₂ peaking before 2030 and carbon neutrality before 2060. A related action plan for transport is expected to be announced before the end of 2022. The country has already set and achieved targets for electric vehicles and ‘new energyvehicles’.
Key figures on transport and climate
Published in Towards Decarbonizing Transport 2023.